Data breaches are in the news nearly every day, making data loss prevention (DLP) top-of-mind for security professionals.
While DLP software has been the default answer since the 1990s for preventing data loss, it’s no longer optimal since company data lives increasingly in the cloud instead of on-premises.
In this guide, you’ll get a refresher on DLP as a practice, insights into why traditional DLP software under performs and a modern approach that your team can implement to prevent data loss.
What is DLP?
Data loss prevention (DLP) is the practice of detecting and preventing data exfiltration. It also represents the software that network administrators employ for monitoring and controlling what data users can transfer.
Unfortunately, DLP as a method has started to fail because traditional software hasn’t advanced enough to mitigate data loss altogether. Legacy DLP tools focus solely on content inspection and lack on contextual inspection – which leaves unstructured data slipping through the cracks.
In their 2023 Market Guide for Data Loss Prevention, Gartner weighed in on this issue, saying, “The DLP market has been saturated with traditional, content-heavy DLP solutions that may not fully cater to the dynamic data security requirements of modern organizations.”
There was a time when traditional DLPs were the optimal solution, but a new era of data protection has emerged.
Why is DLP important?
Before cloud migrations, traditional DLP software worked pretty well at preventing data loss.
Companies with DLPs:
- Met compliance standards: DLP software contained features for enforcing compliance protocols across a business to protect Personally Identifiable Information (PII) and meet HIPAA, PCI-DSS, GDPR and other compliance standards.
- Protected intellectual property (IP): Legacy DLPs helped security teams enact policies to prevent employees from copying or removing IP. Today, stopping IP theft is the use case for which traditional DLP works least as it’s only reactive.
- Improved data visibility: DLP software required security teams to document and classify new and existing data. While this exercise increased data visibility, it also limited a DLP’s capacity to only actions a company defined as bad.
- Reduced financial risk: When company data lived in local drives, DLPs could prevent the chances of a data leak and losing money from damages.
Traditional DLPs undeniably positively impacted the cyber security industry, but they fall short of securing sensitive information as companies continue to transition to cloud technologies and unstructured data increases.
See what Gartner recommends you look for in your DLP solution and what new, more effective solutions are available.
Causes of data leaks
In this rapidly changing, work-from-anywhere world, there are four common causes of data leaks:
Departing employees
Departing employees are a leading cause of data leaks, with 63% of departing employees admitting to stealing corporate data.
As a type of insider threat—a cyber security risk with access to a company’s systems and data—departing employees might have hard feelings and want to expose sensitive information to competitors. Others may want to get a leg up at their new job with contact lists or other templates.
Regardless of motive, insider threats like these are hazardous because they are tough to detect. In 2019, 69% of surveyed organizations reported an insider breach—despite having a DLP.
Unsanctioned app usage
When employees use tools companies don’t protect or monitor, they open the door to leaks.
For example, something as simple as signing up for a free project management tool could harm a business’s finances or reputation. Suppose there are default settings that expose projects publicly. In that case, such an app may reveal product roadmaps or other private company plans to competitors, potentially damaging revenue opportunities, partner relationships and customer trust in their information.
Email and browser-based uploads
The safety of your data depends heavily on the strength of your security perimeter. Malicious actors can intercept email attachments and browser uploads without reliable network protection.
Extrusion by attackers
Cyber attackers seek confidential information and use malware, phishing, smishing, or other methods to access it. Once they’ve collected your data, they can sell it to other criminal organizations or competitors, publicize it or attempt to collect ransom.
How DLP works
DLP manufacturers design their technology to help companies create policies about what employees can and can’t do with data. This software began nearly thirty years ago, and the fundamental premise—developing policies, tagging data, and blocking specific actions—hasn’t changed.
While the tenets of traditional DLP make sense in theory, they aren’t practical in today’s cloud-first world. As Gartner found, 35% of DLP implementations fail before starting.
There are three primary reasons why DLPs no longer work like they used to:
- Data labeling is challenging, bordering on impossible. Implementing data labeling policies effectively or maintaining accurate asset tagging at scale is nearly unattainable. There’s simply too much digital work product created today, and it’s in the hands of every employee.
- Complex data policies can lead to bad user behavior. Employees who just want to get their jobs done will often subvert or circumvent the system, or they may intentionally misclassify data to avoid strict policies.
- Legacy DLPs don’t monitor all data movement. DLP vendors only oversee labeled data, leading to a siloed view of data movement that can miss risky activity.
To avoid executing an ineffective DLP strategy, consider implementing practices that factor in all data in the cloud environment and focus on protecting data rather than preventing loss.
Data protection best practices
Protecting sensitive data and limiting an organization’s cyber security risk starts with following a few strategies:
- Have complete visibility into all file activity—without blocking productivity. By keeping a close eye on all file activity (not users) across computers, cloud and email providers, you can uncover malicious activity before it’s too late.
- Prioritize your highest data risks through automation. Employees have a lot on their plates, making it easy to miss risks simmering under the surface. Automation can bring the most urgent problems to their immediate attention.
- Implement reliable alerts for all data risks. False positives and false negatives can be harmful to your company. Technology with accurate alerts that help you prioritize the events that pose the most significant risk is essential.
- Filter out noise from trusted file activities or scenarios. Always being on high alert is ineffective. Instead, align response tactics to the severity of each event.
It’s essential to note that these practices rely on modern DLP technology, and many existing DLP vendors don’t offer these capabilities since they focus on on-premises workloads.
Types of data loss prevention solutions
There are a few types of data loss prevention solutions and tactics your security team can use:
- Cloud Access Security Broker (CASB) Software: CASBs enforce security policies between cloud service providers and customers. That said, shadow IT and the use of unauthorized cloud-based services threatens a CASB’s effectiveness.
- User and Entity Behavior Analytics (UEBA) Solutions: UEBA is a category of security solutions that help security teams pay close attention to an organization’s network activity by gathering, compiling, and analyzing what employees and contractors do daily. UEBA solutions can be expensive and challenging to understand without adequate training.
- Security Education and Awareness (SEA) Training: Employees are your first line of defense. Teaching and testing them on data prevention best practices can help limit exposure. But cyber attackers are constantly finding new ways to circumvent security measures that employees likely don’t know about.
- Data Loss Prevention (DLP) Software: While these tools prevent data loss in local drives, they don’t perform well in the cloud environment due to the continuous digital product employees create, the need for complex policies and a one-dimensional view of data.
- Insider Risk Management (IRM) Software: This technology, termed by Gartner, employs a modern approach to DLP by mapping and securing sensitive data across quickly changing work environments to overcome the challenges presented by a cloud-first strategy. IRM-based systems help security analysts make sense of an organization’s wealth of data and then make reasonable, informed judgments about whether certain activities are dangerous or not.
Awareness of all the possible mechanisms for protecting your data can help you evaluate what solution would work best for your organization.
Evaluating Insider Risk Management as a solution
For companies that need to be agile, innovative, fast-adapting, and driving major digital transformations internally, it might seem like many DLP technologies fall short. If you’re in that boat, consider exploring an IRM solution.
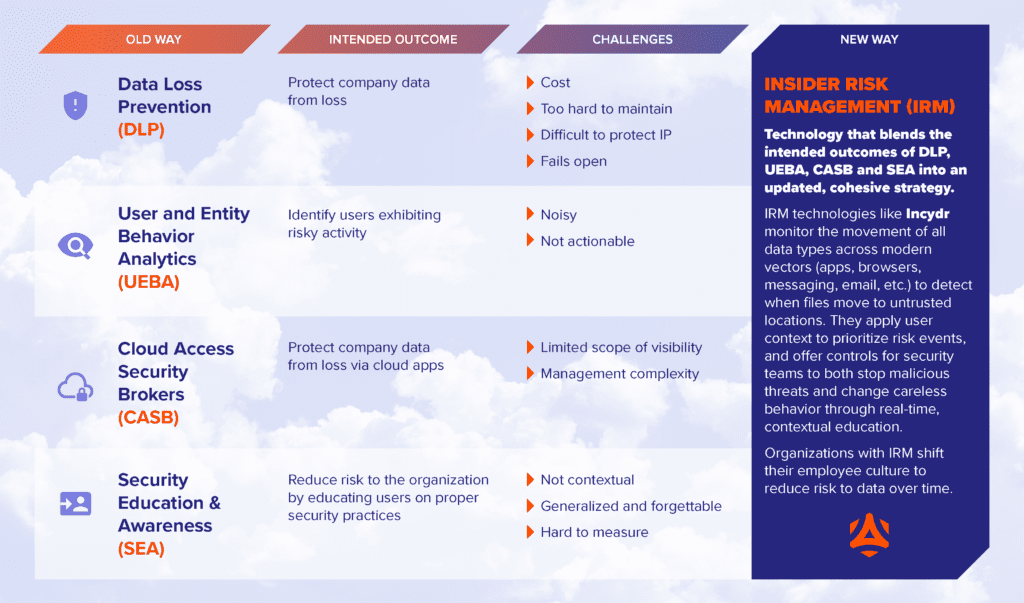
IRMs look at all data, not just the data your company has already labeled. They also prioritize the riskiest actions and have controls that respond to the severity of the data loss event, making it more appropriate for a nuanced environment.
When comparing IRMs, ensure you choose one that secures endpoints, data in motion and cloud data by identifying irregular transfers and movements that are anomalous or suspicious. Code42’s IRM solution Incydr offers this capability, helping admins have more visibility in remote work environments.
Defend against data leaks with a modern approach to DLP
With the transition to cloud technology and hybrid or remote work, every employee endpoint has become its own security perimeter—and security teams have the daunting task of protecting thousands of perimeters from data leaks.
Traditional DLP technology relies on the identifying, classifying and blocking method to obstruct real-time data movement, but this flies in the face of a people-first, innovative and collaborative company.
Thankfully, IRM helps you protect data and fuel digital transformation while safeguarding your competitive edge and employee productivity.
Discover more about IRM today and how it enables security and risk teams to become better business partners, employee facilitators and value creators across the organization.
How is Code42 different from traditional DLP?
Get a side-by-side comparison of Code42 Incydr’s risk-based approach is different from traditional DLP solutions.

