Remote and hybrid work. Adoption of AI tools. Expanded use of contractors. Layoffs and hiring freezes. The workforce is evolving rapidly, which means keeping an organization’s data secure can be a constantly moving target.
That’s where data protection comes into play.
This article provides comprehensive insights into protecting your data — including how to prevent damage to your company’s finances or reputation without disruptive policies that impede employee productivity.
Table of contents
- What is data protection?
- Principles of data protection
- Types of data protection technologies
- Data protection trends
- Notable data protection regulations
- Differences between data protection, security, and privacy
- Data protection strategies
- Streamline security work and minimize employee disruption with Code42 Incydr™
What is data protection?
Data protection is the set of systems and processes that guard an organization’s data against loss, leak, theft, and unavailability. A robust data protection practice monitors all data by sifting through trusted data movements to detect risky behaviors — allowing security teams to use their time efficiently.
Data protection is essential as it helps companies prevent data breaches, exfiltration, downtime, and damage to reputation and finances. Organizations must also enforce data protection to restore lost or corrupted data and meet regulatory requirements.
This practice has become increasingly necessary as workforces grow in volatility and risk unauthorized data removal.
Principles of data protection
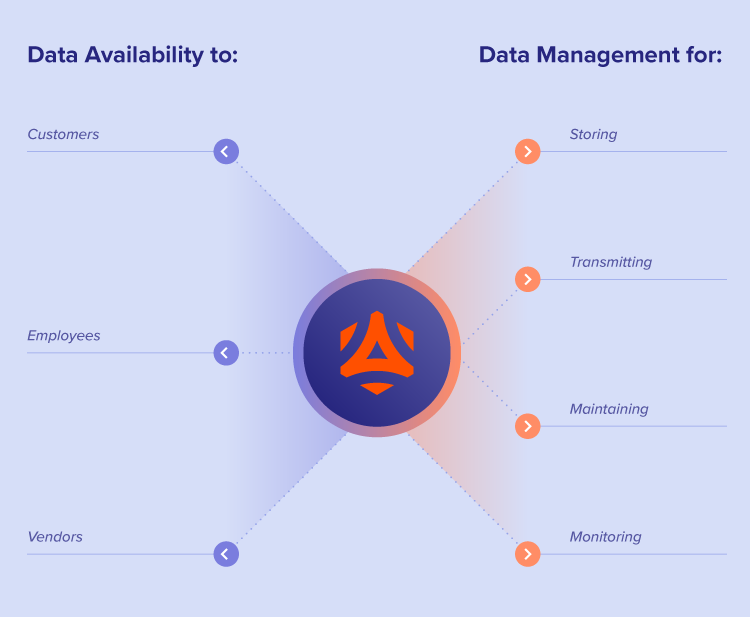
There are two guiding principles of data protection: data availability and data management. Here’s a closer look at these fundamental components.
Data availability
Data availability is the process of ensuring data is available to applications and end users like customers, employees, and vendors when and where they need it.
While data availability might seem independent of other facets of data protection, like security and regulation, it goes hand-in-hand.
Hybrid and remote work has forced companies to adjust security protocols to ensure data is available in situations that traditional on-premise security protocols and firewalls didn’t support — like employees using poorly secured home networks. Another example is collaborating with contractors or vendors, which requires data availability on more cloud storage and applications.
Of course, increased availability necessitates new and innovative data management approaches.
Data management
Data management is the practice of storing, transmitting, maintaining, and monitoring data. This concept is crucial in developing a data protection strategy as it defines how employees and other stakeholders work with data.
With data becoming more available at the permitters of networks such as remote employee laptops and personal cloud applications, data management has taken on a new role. Security teams must now track data movements on these remote devices and applications and understand trends of this activity to detect and flag risky behavior that necessitates intervention.
Types of data protection technologies
Since data protection pertains to security, availability and management, there are many technologies that aim to help companies accomplish these goals:
- Tape or disc-based backups: This technology consists of physical devices that security teams use to store or “back up” data assets.
- Storage snapshots: In the form of an image or other reference point, storage snapshots reflect data at a specific point in time.
- Continuous data protection (CDP): Also called continuous backup, CDP is a system that backs up data on a computer system every time someone makes a change.
- Firewalls: These devices monitor traffic to or from a network. They allow or block traffic based on a defined set of security rules.
- Encryption: Encryption is the process of securely converting data to and from scrambled text so you can store or transfer it between devices without compromising the raw information.
- Endpoint protection: This data protection technology focuses on monitoring and preventing threats on endpoint devices — items on the edge of a network — like laptops and mobile phones.
- Identity and Access Management (IAM): IAM systems provide a framework for businesses to manage digital identities and user access to different data and systems, ensuring that only authorized individuals can access sensitive information. This strategy is critical for minimizing the risk of data breaches and maintaining compliance with data protection regulations.
- Data loss prevention (DLP): DLP solutions detect potential data leaks and exfiltration. They require extensive classification of data in order for network administrators to monitor and control what data users transfer. Data goes unmonitored by a DLP if it is not classified by the company.
- Insider Risk Management (IRM): IRM solutions are a risk-based approach to data protection. Unlike conventional DLP methods, IRM solutions monitor all data, not just data a company has already labeled, making it an ideal approach to managing a quickly changing workforce. IRM helps security teams prioritize what data matters most to their unique needs and respond promptly to data risks without impeding employee productivity.
Awareness of all the possible technologies for protecting your data can help you evaluate what solution would work best for your organization.
Data protection trends
As computing environments evolve, several new trends are emerging that are affecting the data protection landscape:
The rise of AI and machine learning
One notable trend in data protection is the increased reliance on artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning technologies. These tools are becoming crucial in the detection and prevention of data breaches before they occur. By analyzing patterns and predicting potential security threats with greater accuracy, AI and machine learning can offer proactive solutions to data protection, significantly reducing the risk of data loss or IP theft.
In addition, businesses need to address the risk of data leaks via AI tools, most likely using their existing processes or technology.
Enhanced privacy regulations compliance through automation
With the continual evolution and tightening of data privacy laws globally, organizations are turning to automated solutions to ensure compliance. Automated compliance tools can monitor and manage data in real-time, ensuring that any data collected, stored, or processed adheres to the latest regulations without the need for manual oversight. This trend not only helps in mitigating legal risks and fines but also builds trust with customers by upholding high privacy standards.
Zero trust architecture becomes the norm
The principle of “never trust, always verify” is becoming more embedded in data protection strategies, making Zero Trust architecture a standard approach. This model assumes that threats can exist inside and outside the network, thus requiring strict identity verification from anyone trying to access resources in the network, regardless of their location. The adoption of Zero Trust minimizes the attack surface and provides organizations with more control over their data and resources, which is essential in a hybrid work environment.
Notable data protection regulations
The trends and changes in data protection aren’t only of interest to companies and their security teams. Governments worldwide are diving into data privacy and security regulations, significantly impacting how these systems operate.
Some of the most prominent laws include:
GDPR in the European Union (EU)
The General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) is an EU law published in 2016 that gives individual users of digital services more rights and control over their personal information used by corporations and other organizations.
Companies that operate in or work with countries in the EU that don’t comply with these regulations are subject to steep fines — up to 4% of a company’s global revenues or 20 million Euros.
Data protection laws in the U.S.
Unlike the EU, the U.S. has no single principal data protection legislation. Instead, hundreds of federal and state laws aim to protect Americans’ data. Here are a few examples of those laws:
- The Federal Trade Commission Act: This law prohibits unfair methods of competition and requires organizations to respect consumer privacy.
- The Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA): HIPAA regulates health information storage, confidentiality and use.
- The California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA): This 2018 law gives Californians the right to know about the personal information companies collect about them, request deletion of such data and opt out of its sale.
As data protection continues to grow as a priority in an increasingly digital world, U.S. laws will likely evolve in the years ahead. For example, with AI and machine learning rapidly advancing, the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) is spearheading efforts to establish comprehensive regulations – although this is still evolving. The NIST aims to set a foundational framework for the ethical and efficient use of AI technologies across various sectors.
CPS 234 in Australia
Australia introduced the Prudential Standard CPS 234 in 2019 to regulate how organizations in the finance and insurance sectors protect their information security from cyber threats. It also requires strict auditing reporting systems to be in place to ensure systems stay compliant.
Differences between data protection, security, and privacy
While people in your organization may use the terms data privacy, data security, and data protection interchangeably, there are some critical differences between them:
- Data privacy: This practice focuses on controlling who has access to sensitive data, often personal, and relies on data protection regulations to achieve compliance.
- Data security: A subset of data protection, data security is the practice of protecting the integrity of data against manipulation and risky behavior from external and internal threats.
- Data protection: As outlined in this guide, data protection is the set of systems and processes that protects data from misuse, ensuring it’s available to those permitted to use it while supporting employee productivity.
Knowing the differences between these terms can help prevent misunderstandings, especially when collaborating with departments outside of the security team.
Data protection strategies
Implementing robust data protection strategies is crucial for organizations to secure sensitive data, ensure compliance with regulations, and safeguard against potential data loss or theft. Here are key strategies that organizations should consider:
- Use encryption and access controls: Encrypting data at rest and in transit provides a strong layer of protection, making it unreadable to unauthorized users. Implementing stringent access controls, based on the principle of least privilege, ensures that only authorized personnel have access to sensitive data. This not only protects against external threats but also minimizes the risk of insider threats.
- Regularly update software and systems: This is crucial for safeguarding against emerging threats. By patching vulnerabilities, organizations can close security gaps that could be exploited by cybercriminals. Employing secure configurations further minimizes the risk of unauthorized access or data breaches. This comprehensive strategy provides robust protection across all organizational levels, ensuring that sensitive data remains secure.
- Evaluate external vs internal data risks: Understanding your external and internal data risks is crucial for improving your organization’s cybersecurity posture. External risks can be addressed by using advanced technology systems for threat detection and response, such as intrusion detection systems (IDS), firewalls, and anti-malware solutions. Internal risks can be trickier to see without complete visibility into data exfiltrations, but to start, ensure that vendors and partners adhere to stringent data protection standards through contracts and regular audits. By proactively identifying and mitigating both external and internal risks, companies can safeguard against data breaches and protect the business’ most sensitive data (and reputation).
- Educate employees on policies and security awareness: Aligning organizational policies with the evolving landscape of threats and regulations, with a keen focus on the human element, is essential. Employees should be well versed in company data protection policies, identifying security threats, and implementing safe data handling practices at work. Regular, ongoing training can foster a culture that prioritizes security awareness and reduce data breaches stemming from human error.
Streamline security work and minimize employee disruption with Code42 Incydr™
Unlike traditional DLP approaches, Code42 Incydr is a data protection solution that moves beyond pre-identifying and outright blocking all data exfiltration. Incydr protects high value data like source code, customer data, and more by monitoring data movement across all endpoints, browsers, and cloud services, and prioritizes actions to swiftly address high-risk incidents.
According to Forrester’s Total Economic Impact study, Incydr has been proven to halve the time required to investigate high-risk security threats. And with integrated security lessons, Incydr immediately addresses and amends user behavior to reduce common security errors made by employees. This allows security teams to focus their efforts on preventing the most critical data leaks.
